Effect of Dexmedetomidine on Hemodynamics in Thoracic Surgery - A Randomized Controlled Study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/jcram.1.1.2Keywords:
Double Lumen Tube, Mean Arterial Pressure, PropofolAbstract
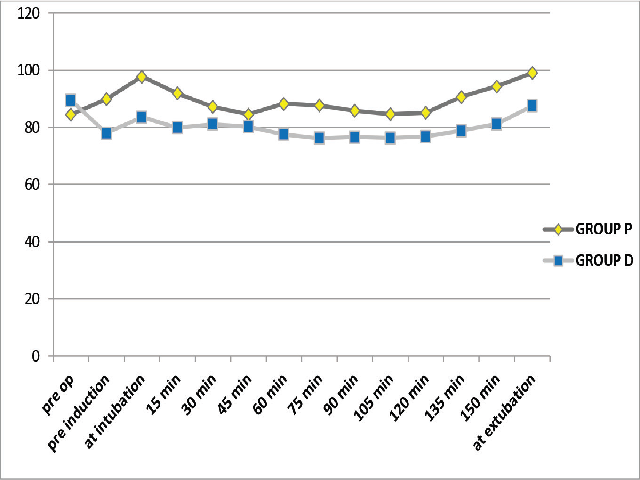
Background: Thoracotomy is associated with various hemodynamics consequences that are influenced by the position of the patient’s body on the operation Table and metabolic functions of lungs. Dexmedetomidine is an alpha-2 agonist sedative-analgesic that inhibits endogenous norepinephrine release and has been used in various studies to maintain intraoperative hemodynamic stability. Aim: To evaluate the effect of Dexmedetomidine infusion on hemodynamics during thoracic surgery. Methods: The selected patients were randomly allocated to the two groups (39 patients in each group) using a computer-generated random number table. Group D patients received initial bolus of Dexmedetomidine 1 μgm/kg in 100 ml normal saline over 15 min before induction followed by intravenous infusion of dexmedetomidine @ 0.5 μgm/kg/hr intraoperatively. Group P received initial 100 ml normal saline over 15 min given prior to induction followed by infusion of Propofol @ 200 μgm/kg/min intraoperatively. Statistics: All analysis was performed on SPSS (Windows version 16). Results: In this study, it was observed that use of dexmedetomidine result in less rise in MAP and heart rate at the time of intubation as well as at the time of extubation in comparison to propofol (p<0.05). Episodes of bradycardia was more in D Group as 12.8% patients required atropine for bradycardia compared to only 2.5% in group P. As well as more patients in Group D received mephentermine for hypotension. The intraoperative requirement of fentanyl was also more in group P. Conclusion: Initial bolus of Dexmedetomidine 1 μg/kg 15 min before induction followed by intravenous infusion of Dexmedetomidine @ 0.5 μg/kg/hr decreases the stress response during DLT intubation and extubation but more patients in dexmedetomidine group required atropine or mephentermine for bradycardia and hypotension.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
JCRAM and its contents are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial-No Derivs 4.0 License. Permissions beyond the scope of this license may be available with editor@jcramonline.com






