Efficacy and Safety of Methotrexate Plus Leflunomide in Patients of Rheumatoid Arthritis not Responding to Methotrexate Alone
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/jcram.3.1.2Keywords:
Rheumatoid arthritis, RA, Methotrexate, Leflunomide,Abstract
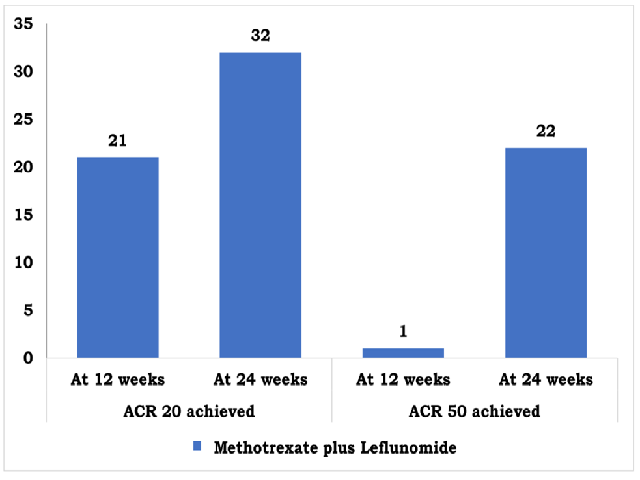
Introduction: Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory disease affecting approximately 0.24% of the global population and can lead to joint destruction, functional decline, disability, and decreased quality of life. According to ACR and EULAR guidelines, patients with RA should initiate treatment with conventional synthetic Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (csDMARDs), such as Methotrexate (MTX). In patients with an inadequate response to csDMARDs, it is recommended to add a targeted synthetic DMARD, such leflunomide or a biologic DMARD (bDMARD), such as tumor necrosis factor inhibitor (TNFi). Objectives: To study the efficacy and safety of methotrexate and leflunomide in patients of Rheumatoid arthritis not responding to methotrexate alone. Materials and Methods: It was a single centre, observational study in 50 patients of Rheumatoid Arthritis taking methotrexate plus leflunomide after inadequate response to methotrexate monotherapy (15mg/week) for 12 weeks. Patients were included in the study after meeting inclusion and exclusion criteria. Patients were taking leflunomide in a dose of 10 mg/day and methotrexate in a dose of 15 mg/week with Folic acid 5 mg/week. Efficacy outcomes; ACR 20/50/70 and DAS-28 CRP based remission/low disease activity were assessed at 12 weeks and 24 weeks. Statistical analysis was done using Jamovi (V2.3.18) software. Results: Improvement from baseline to weeks 12 and 24 was observed for all efficacy outcomes (including ACR 20/50 and DAS-28 CRP based low disease activity/remission) in patients taking methotrexate plus leflunomide. At 24 week 64% achieved ACR-20, 44% patients achieved ACR-50, 24% patients achieved Low Disease activity (LDA) and 6% patients achieved remission. The most common adverse effect was nausea and vomiting at 24 weeks. No deaths were reported. Conclusion: In our study methotrexate and leflunomide conferred improvement in disease activity measures and functional outcomes after 24 weeks of treatment.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
JCRAM and its contents are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial-No Derivs 4.0 License. Permissions beyond the scope of this license may be available with editor@jcramonline.com






